Pioneering in safety, the first seismic isolation structure in the world
- mr-k
- Uncategorized
The First Seismic Isolation Structure in the World at the Tomb of Cyrus: Pioneering Safety and Architecture”
The Tomb of Cyrus the Great, one of the most prominent historical monuments of Iran and the world, is recognized as the first earthquake-resistant structure, or more precisely, a structure equipped with a base isolation system. Although this tomb is not officially acknowledged as the earliest use of modern seismic technologies, it can be considered an example of humanity’s pioneering efforts in utilizing principles similar to today’s seismic isolation systems employed in earthquake-resistant buildings.
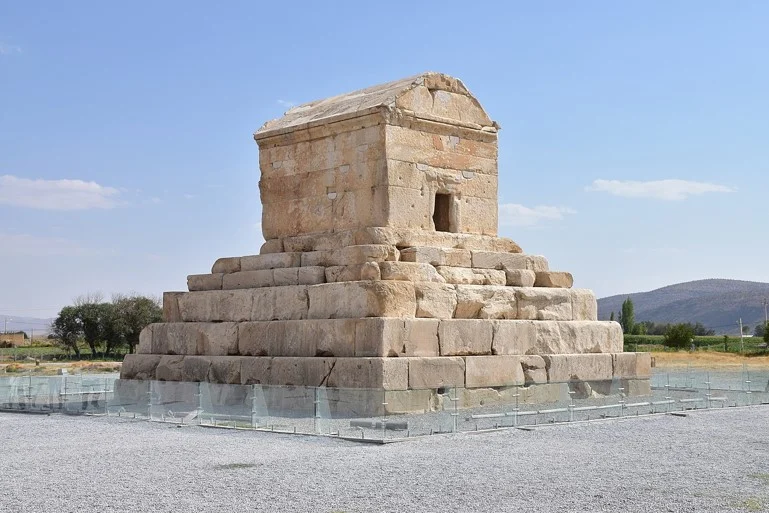


The Tomb of Cyrus the Great and Earthquake-Resistant Design Principles
The Tomb of Cyrus, located in Pasargadae, is one of the outstanding architectural structures of ancient Iran. Due to its unique construction, this tomb was designed to be resistant to earthquakes and other natural forces. Although modern scientific concepts such as seismic isolation did not exist at the time, the distinctive design of this tomb clearly demonstrates that the engineers of that era utilized principles similar to those employed today to counter earthquake forces.
One of the remarkable features of the Tomb of Cyrus is the use of large and sturdy stones as the foundation of the structure, which function in a way similar to modern base isolation systems. These stones, meticulously and precisely stacked upon one another, essentially created a resilient base for the tomb capable of absorbing and dissipating seismic forces. This characteristic not only enhanced its resistance to earthquakes but also effectively ensured the structure’s safety against ground movements.
Base Isolators and Their Parallels with the Tomb of Cyrus
Base isolators are considered one of the most advanced earthquake-resistant systems in the modern world, typically installed beneath critical and sensitive structures. These systems are designed to absorb seismic energy and prevent its transfer to the building. Essentially, base isolators act as a separating layer that minimizes the impact of ground vibrations on the structure.
These modern features bear significant resemblance to the design principles of the Tomb of Cyrus. Just as the tomb utilized large and sturdy stones to naturally enhance its earthquake resistance, today’s base isolator systems achieve this resilience through advanced materials and cutting-edge technologies, elevating the precision and effectiveness of such mechanisms to entirely new levels.

The Significance of This Pioneering Effort
The pioneering nature of the Tomb of Cyrus in applying earthquake-resistant principles reflects the profound understanding ancient engineers had of nature and their ability to utilize available resources to address natural challenges. It demonstrates that the pursuit of constructing earthquake-resistant structures is not exclusive to the modern era but has deep roots in the history of human architecture.
The Tomb of Cyrus is not only a historically and culturally significant ancient monument but also an engineering marvel that can be considered an early example of scientific and seismic-resistant thinking. The fact that this tomb has withstood earthquakes for thousands of years serves as a testament to the effectiveness of its design and the precision of the engineers of that time.

Conclusion
Although the Tomb of Cyrus is not directly recognized as the first use of base isolation in the world, its design and application of principles similar to modern seismic-resistant systems highlight the engineering ingenuity of ancient times. This tomb, as a symbol of the scientific and engineering capabilities of the ancient world, can serve as an inspiration for modern architects and engineers in advancing building safety and earthquake resistance.